二叉树前中后向遍历 Binary Tree Front, Middle, and Post Order Traversal
Idea
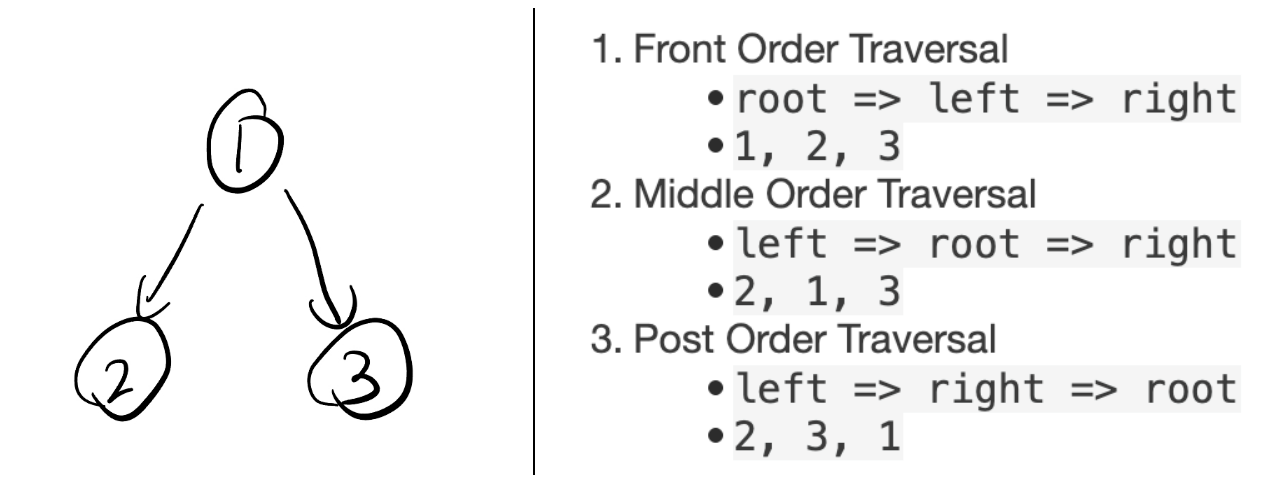
Front, Middle, and Post Order Traversal
Traversal Recursion Template
Middle-order traversal
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
res = []
def dfs(node):
if node == None:
return None
# Front-order traversal
res.append(node.val)
if node.left:
dfs(node.left)
# Middle-order traversal
# res.append(node.val)
if node.right:
dfs(node.right)
# Post-order traversal
# res.append(node.val)
return None
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
dfs(root)
print(res)
# front: [1, 2, 3]
# middle: [2, 1, 3]
# post: [2, 3, 1]
Traversal Iteration Template
在递归中,节点的访问关系是存在函数调用栈中的。
如果我们想用迭代的方法来实现树的前中后序访问,我们需要一个栈,以及记录节点被访问与否。
- Approach 1,在 root 节点上压入 null 节点来辨别 root 节点。
- Approach 2,用一个 visited map 来记录已经 加入结果集/被访问 的节点。
下面代码为中序遍历,在 root 节点上压入 null 节点来辨别 root 节点。
def iterateTree(node):
res = []
stack = []
if node != None:
stack.append(node)
while len(stack) > 0:
# Check if the top of the stack is None
cur = stack[-1]
if cur != None:
cur = stack.pop()
# # Post-order traversal
# stack.append(cur)
# stack.append(None)
if cur.right != None:
stack.append(cur.right)
# # Middle-order traversal
# stack.append(cur)
# stack.append(None) # The middle node is visited but not yet processed, use a Null Node to mark it
if cur.left != None:
stack.append(cur.left)
# Front-order traversal
stack.append(cur)
stack.append(None)
else:
# If the top of the stack is None, it means we append the node to the result list
stack.pop()
cur = stack.pop()
res.append(cur.val)
return res
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
print(iterateTree(root))
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
My Recursion Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def isBST(root, low, high):
if root == None: return True
if root.val >= high or root.val <= low: return False
isLeftValid = isBST(root.left, low, root.val)
isRightValid = isBST(root.right, root.val, high)
return isLeftValid and isRightValid
return isBST(root, float("-inf"), float("inf"))
Front Order Traversal
We can pass the root's value to subnodes
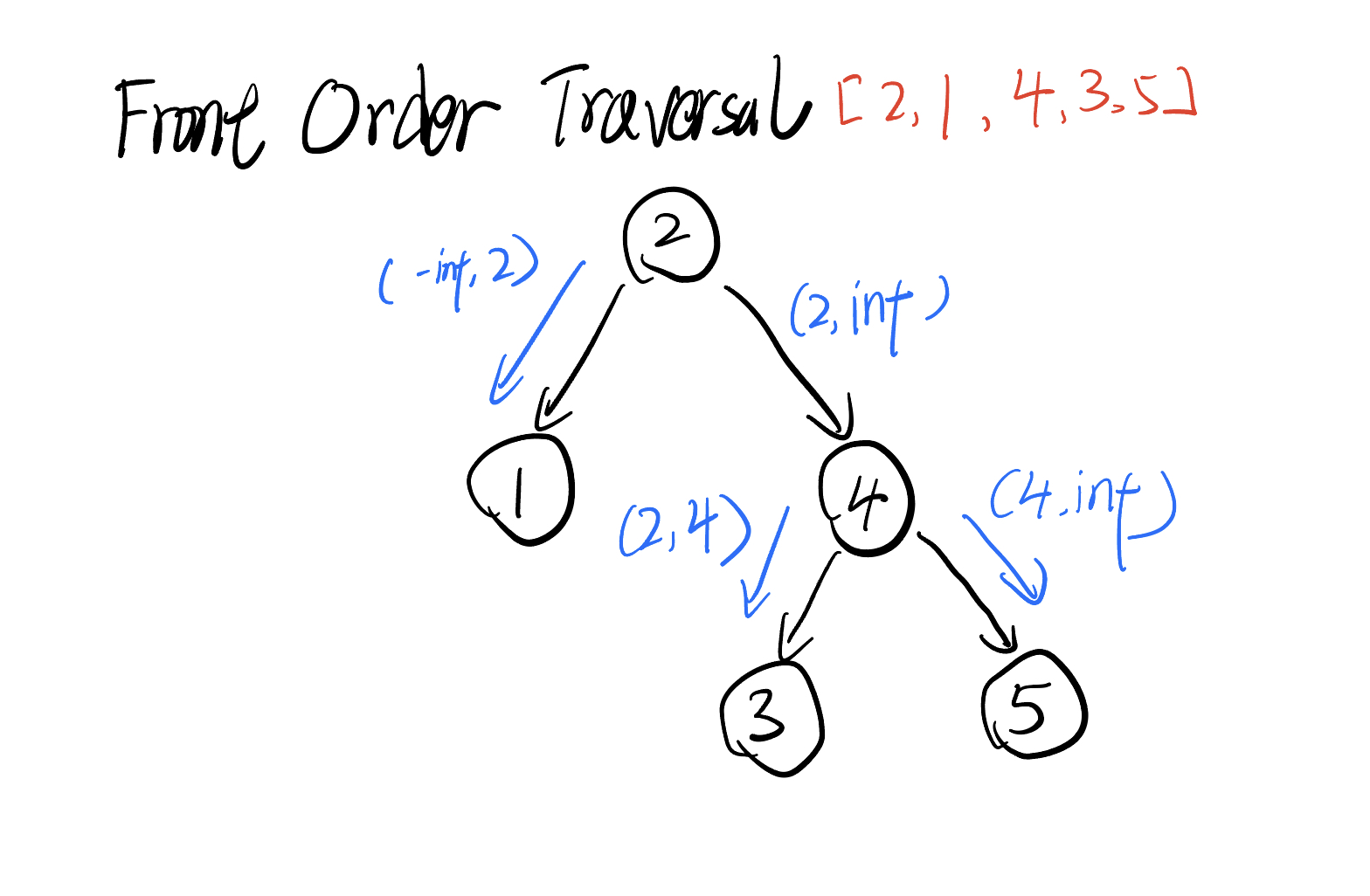
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], left=-inf, right=inf) -> bool:
if root == None:
return True
return left < root.val < right and self.isValidBST(root.left, left, root.val) and self.isValidBST(root.right, root.val, right)
Middle Order Traversal
It is like iterating through a monotonically increasing array
- The current node's value must be smaller than previous node's value
- The initial previous node's value is
-infto ensure the first node's value is valid
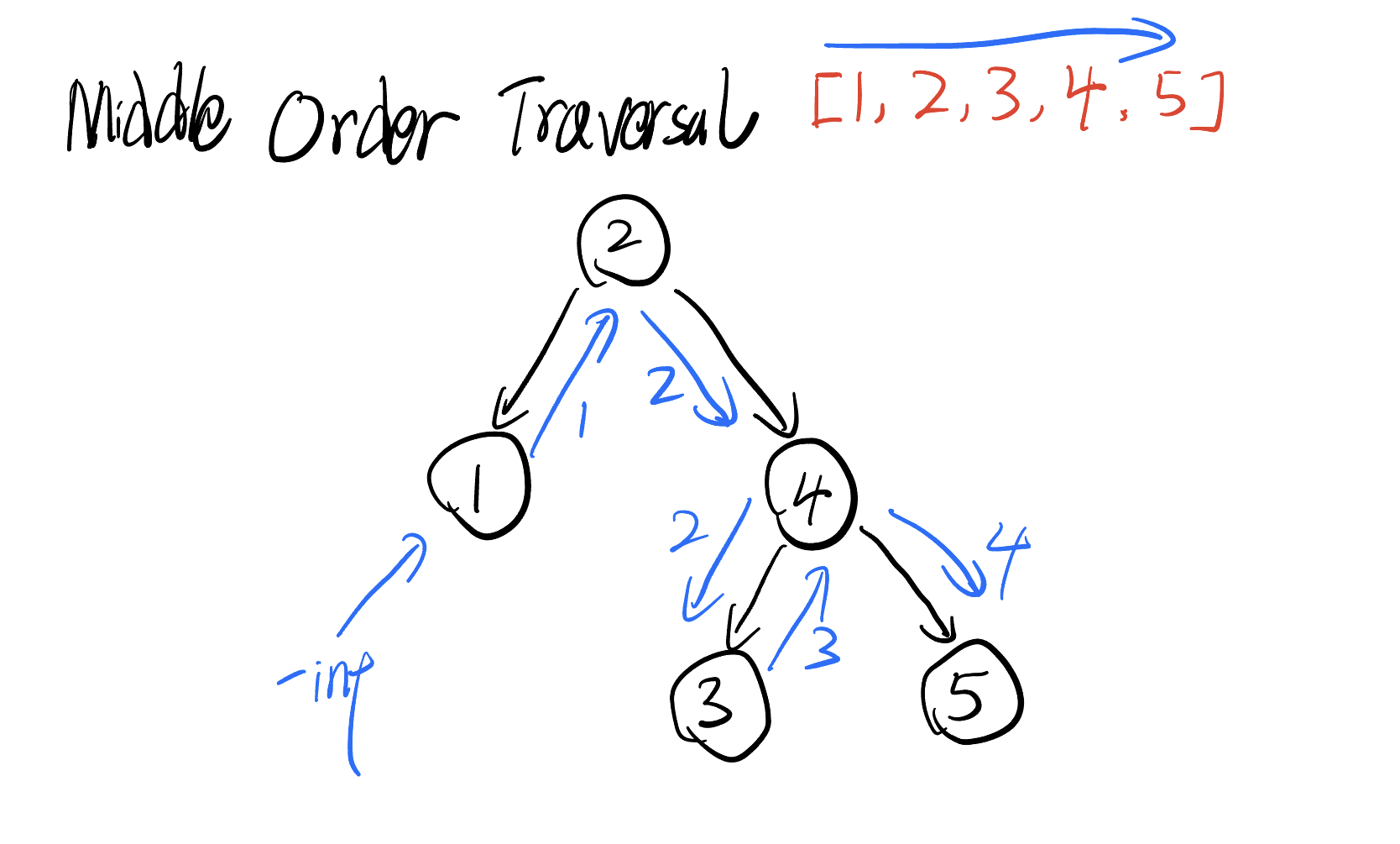
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
minValue = -inf
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if root == None:
return True
if self.isValidBST(root.left) == False:
return False
if self.minValue >= root.val:
return False
self.minValue = root.val
if self.isValidBST(root.right) == False:
return False
return True
Post Order Traversal
Needs to return the valid values range for checking
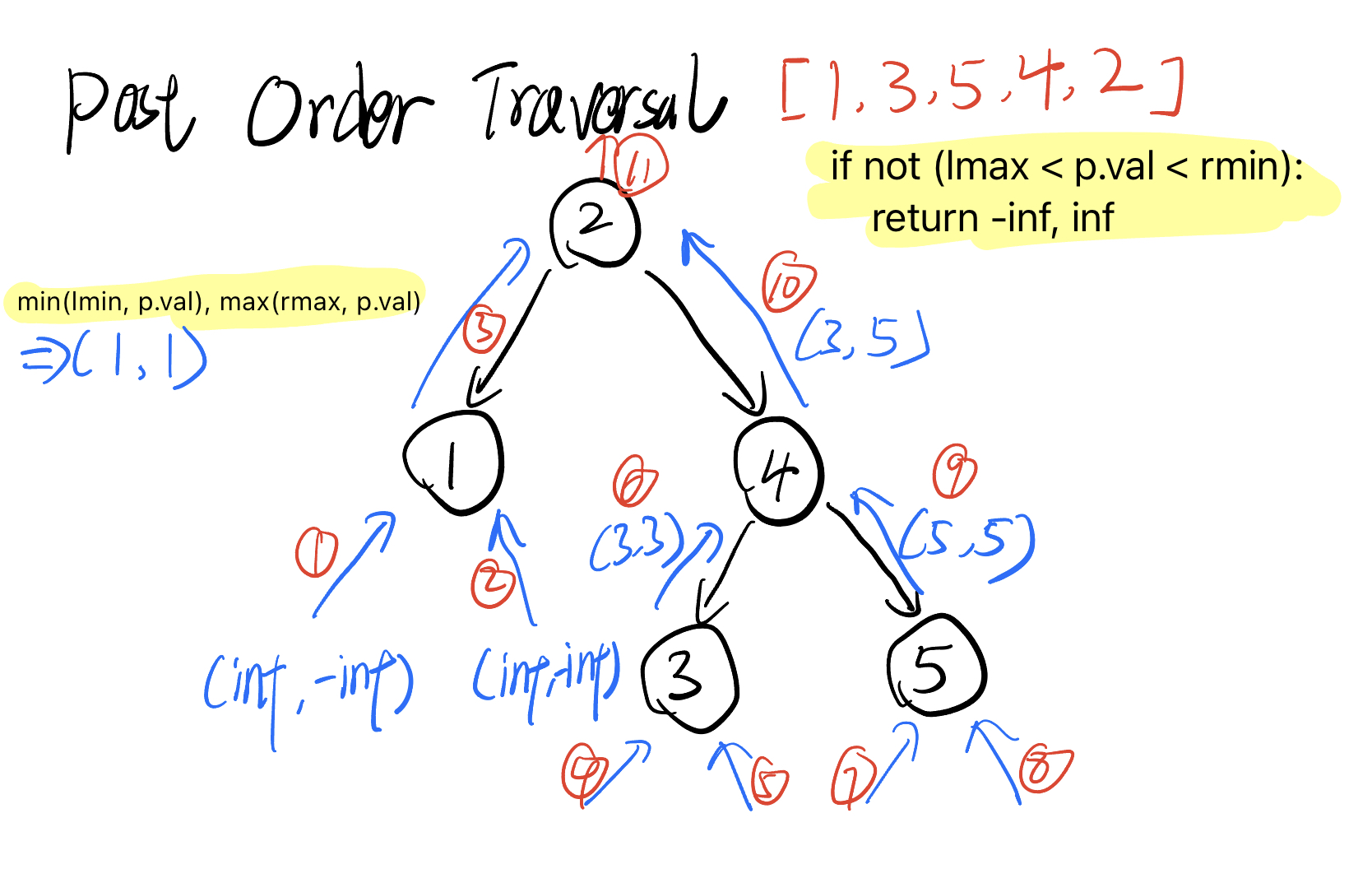
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def check(p):
if p == None:
return inf, -inf # Ensure the validation of Node with Empty subNode
lmin, lmax = check(p.left)
rmin, rmax = check(p.right)
if not (lmax < p.val < rmin):
return -inf, inf
return min(lmin, p.val), max(rmax, p.val)
return check(root)[1] != inf
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not preorder:
return None
rootVal = preoder[0]
leftLen = inorder.index(rootVal)
left = self.buildTree(preorder[1:1+leftLen], inorder[:leftLen])
right = self.buildTree(preoder[1+leftLen], inorder[1+leftLen:])
return TreeNode(preoder[0], left, right)