反转链表系列 Linked List Reverse Series
Idea
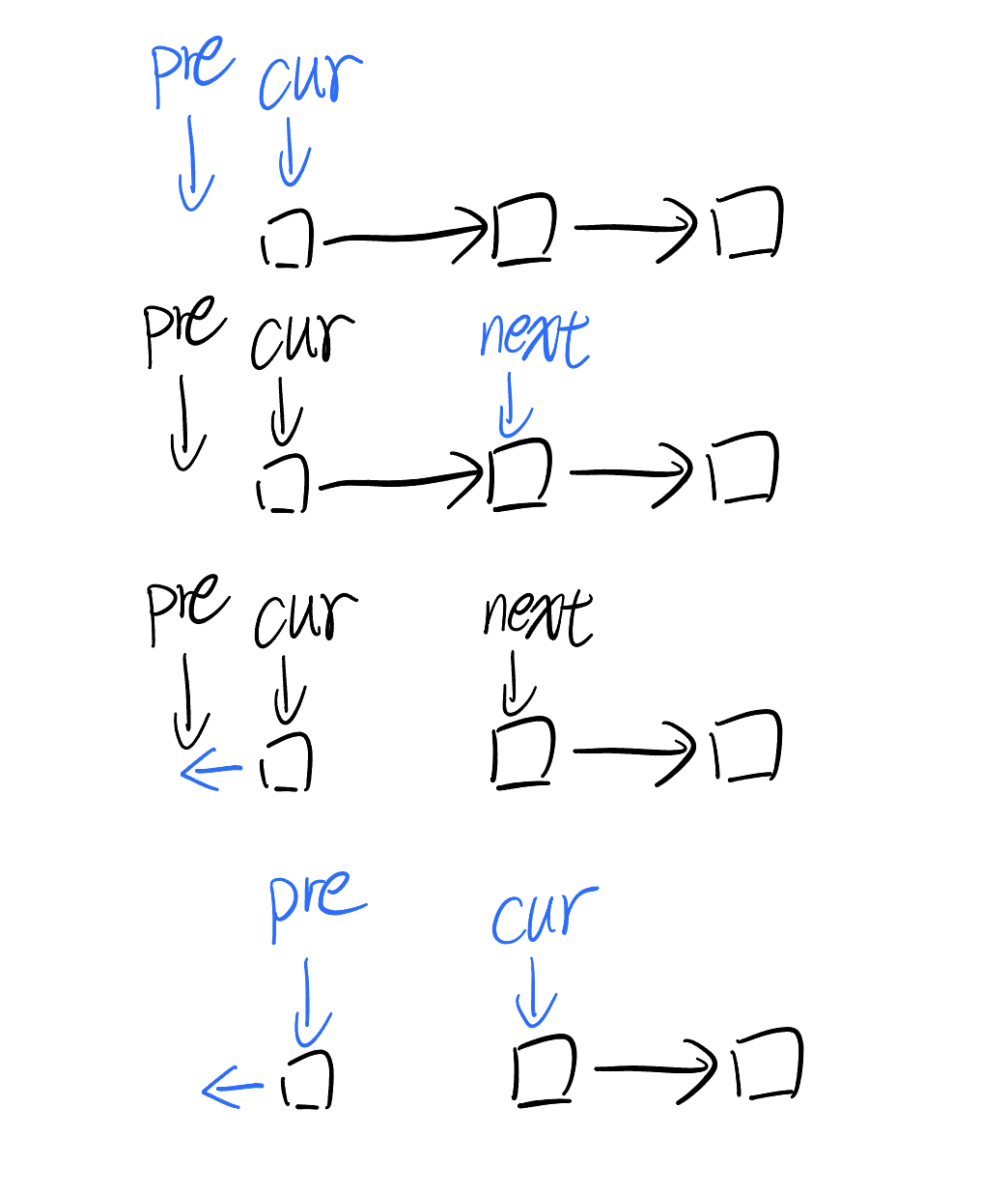
Reverse linked list
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# dummy = ListNode(0, head)
cur = head
prev = None
while cur:
next = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = next
return prev
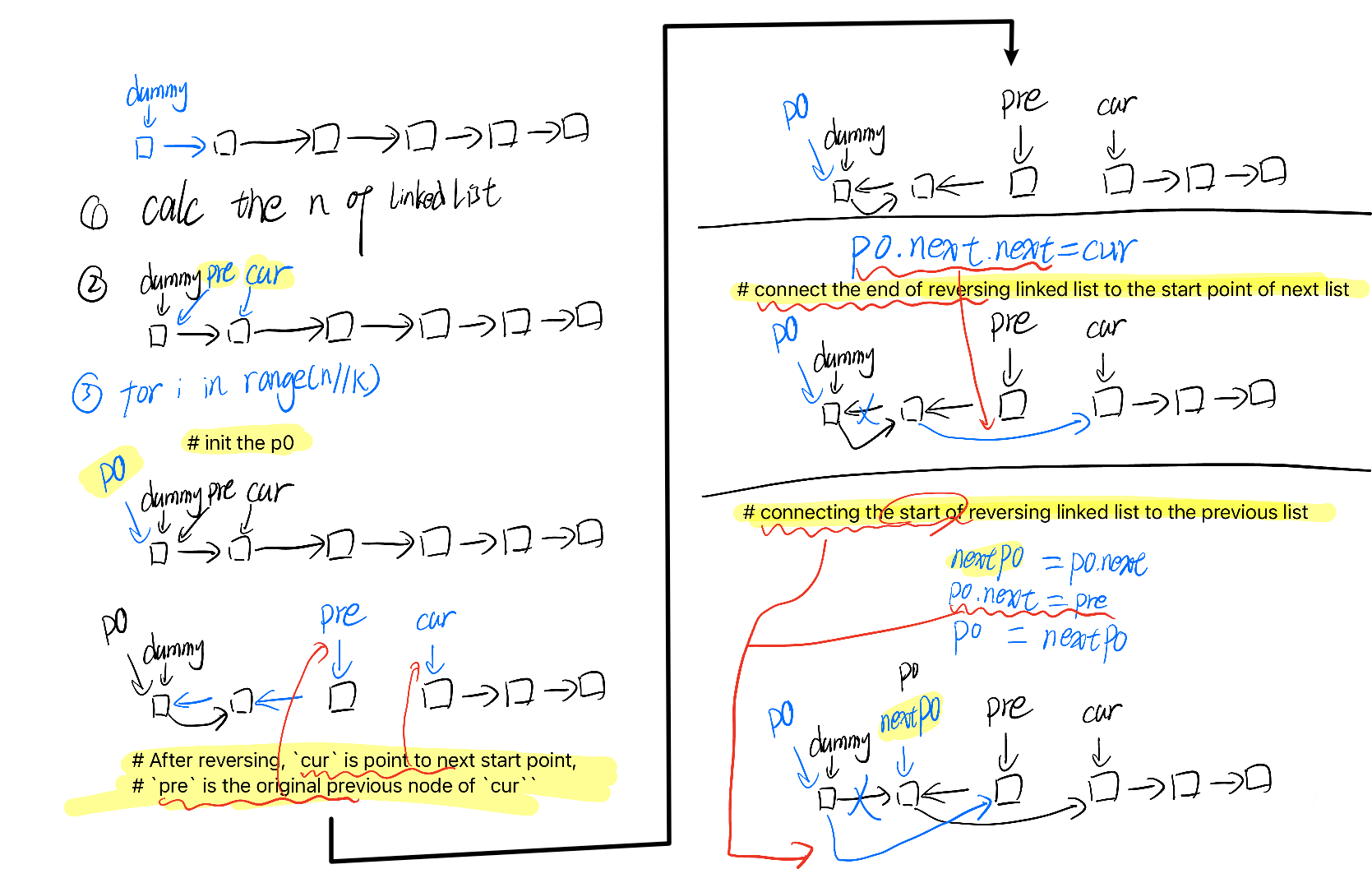
Reverse Nodes in K-Group
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
pre = dummy
cur = head
# 1. Calc the length of linked list
n = 0
while cur:
cur = cur.next
n += 1
cur = head
for i in range(n//k):
# init the p0
p0 = pre
for j in range(k):
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nxt
# After reversing, `cur` is point to next start point,
# `pre` is the original previous node of `cur``
# connect the end of reversing linked list to the start point of next list
p0.next.next = cur
# cache the end of reversing linked list
nxtP0 = p0.next
# connecting the start of reversing linked list to the previous list
p0.next = pre
pre = nxtP0
return dummy.next
206. Reverse Linked List
prev = pre
next = nxt
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# dummy = ListNode(0, head)
cur = head
prev = None
while cur:
next = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = next
return prev
92. Reverse Linked List II
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: Optional[ListNode], left: int, right: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
cur = head
pre = dummy
for i in range(left-1):
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
p0 = pre # p0 is the node before the reversed starting node
# leftNext = cur # p0.next
for i in range(right-left+1):
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nxt
p0.next.next = cur
p0.next = pre
return dummy.next
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
pre = dummy
cur = head
# 1. Calc the length of linked list
n = 0
while cur:
cur = cur.next
n += 1
cur = head
for i in range(n//k):
# init the p0
p0 = pre
for j in range(k):
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nxt
# After reversing, `cur` is point to next start point,
# `pre` is the original previous node of `cur``
# connect the end of reversing linked list to the start point of next list
p0.next.next = cur
# cache the end of reversing linked list
nxtP0 = p0.next
# connecting the start of reversing linked list to the previous list
p0.next = pre
pre = nxtP0
return dummy.next
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
pre = dummy
cur = head
while cur:
p0 = pre
for i in range(2):
if cur == None:
break
next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
p0.next.next = cur
preTmp = p0.next
p0.next = pre
pre = preTmp
return dummy.next
2816. Double a Number Represented as a Linked List
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def doubleIt(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def reverseList(head):
cur = head
pre = None
while cur:
next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
return pre
def addTwoLists(headA, headB):
curA = headA
curB = headB
quotient = 0
while curA and curB:
curSum = curA.val + curB.val + quotient
quotient = curSum // 10
remain = curSum - quotient*10
curA.val = remain
if curA.next == None:
if quotient != 0:
curA.next = ListNode(quotient)
break
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
return headA
rHead = reverseList(head)
dHead = addTwoLists(rHead, rHead)
return reverseList(dHead)
445. Add Two Numbers II
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def reverseList(head):
cur = head
pre = None
while cur:
next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
return pre
def addTwoLists(headA, headB):
curA = headA
curB = headB
quotient = 0
while curA and curB:
curSum = curA.val + curB.val + quotient
quotient = curSum // 10
remain = curSum - quotient*10
curA.val = remain
if curA.next == None:
if curB.next != None:
curA.next = ListNode(0)
elif quotient != 0:
curA.next = ListNode(quotient)
break
elif curB.next == None:
curB.next = ListNode(0)
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
return headA
rl1 = reverseList(l1)
rl2 = reverseList(l2)
al1 = addTwoLists(rl1, rl2)
ral1 = reverseList(al1)
return ral1
2. Add Two Numbers
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def reverseList(head):
cur = head
pre = None
while cur:
next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
return pre
def addTwoLists(headA, headB):
curA = headA
curB = headB
quotient = 0
while curA and curB:
curSum = curA.val + curB.val + quotient
quotient = curSum // 10
remain = curSum - quotient*10
curA.val = remain
if curA.next == None:
if curB.next != None:
curA.next = ListNode(0)
elif quotient != 0:
curA.next = ListNode(quotient)
break
elif curB.next == None:
curB.next = ListNode(0)
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
return headA
al1 = addTwoLists(l1, l2)
return al1
ENG
kis a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple ofkthen left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.- the number of nodes is not a multiple of
kthen left-out nodes - should remain as it is.
- the number of nodes is not a multiple of