PEFT - LoRA
参数高效微调(Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tune,PEFT)
List
-
LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685 降低模型超参数调优的成本
-
dLoRA: Dynamically Orchestrating Requests and Adapters for LoRA LLM Serving https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi24/presentation/wu-bingyang 动态调度request和adapter(merge/unmerge),提高GPU使用率和请求吞吐量
-
Fairness in Serving Large Language Models https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi24/presentation/sheng 公平的负载均衡,确保GPU利用率。确保低负载用户请求被满足(不starve),高负载用户用户在GPU可用的情况下可以被尽可能满足。
-
S-LoRA,并行推理上千个LoRA Adapters
-
SLoRA,LoRA在
LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)2021
问题:
- 大模型 full fine-tuning 需要训练所有的参数,不可行。比如要部署GPT3 175B 模型实例成本非常高
解决方案
-
冻结预训练模型的权重,将可训练的低秩分解矩阵注入模型的每一层
- 在LORA的策略下,增加了右侧的“旁支”,也就是先用一个Linear层A,将数据从d dd维降到r,这个r也就是LORA的秩,是LORA中最重要的一个超参数。一般会远远小于d
-
大大减少可以训练的参数量
-
elimination of adapter inference latency by directly merging the adapter with the model parameters
-
多模型支持
- swapping adapters by adding and subtracting LoRA weights from the base model.
效果
- 与使用 Adam fine-tune 的 GPT-3 175B 模型相比,LoRA 能够减少 10000X 的可训练参数,减少 3 倍的 GPU 内存需求。
- 与 adapters 不同,LoRA 的需要训练的参数少,并且没有额外的推理延时。
问题
- 串行LoRA请求延时低
- 并行LoRA请求的吞吐量很低,因为需要swap adapater
- 没有考虑用 host memory 来提可服务的 LoRA 的数量
开源代码 https://github.com/microsoft/LoRA
论文 https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685
一个矩阵的秩越大,其信息含量越大。秩是矩阵中线性独立的数目
本质是大矩阵等于两个小矩阵的乘积
- 可以参考 sd_scripts/lora.py 中,在 FFN 中先降维计算再升维的过程
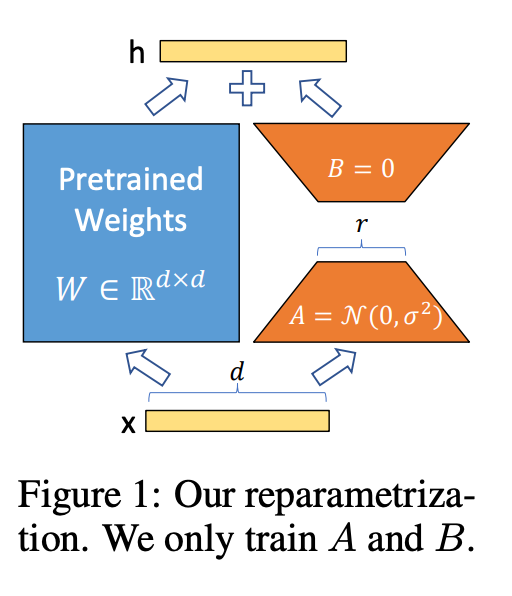
缺点
- 无法在单 batch 进行多个不同任务的处理。
- 多个 LoRA 没法同时merge到一个模型上,模型加载到显存后只能对一个 batch 加载一个 LoRA 参数,对于云端部署推理的时候,对于多任务部署时可能 batch 没法打满,减缓推理速度。
- 不具备非线性能力
- 使用 LoRA 时需要将 BA 矩阵 merge 回原始模型,在尝试对 BA 中间加入非线性变换后,发现整个结果变得很差
Orch
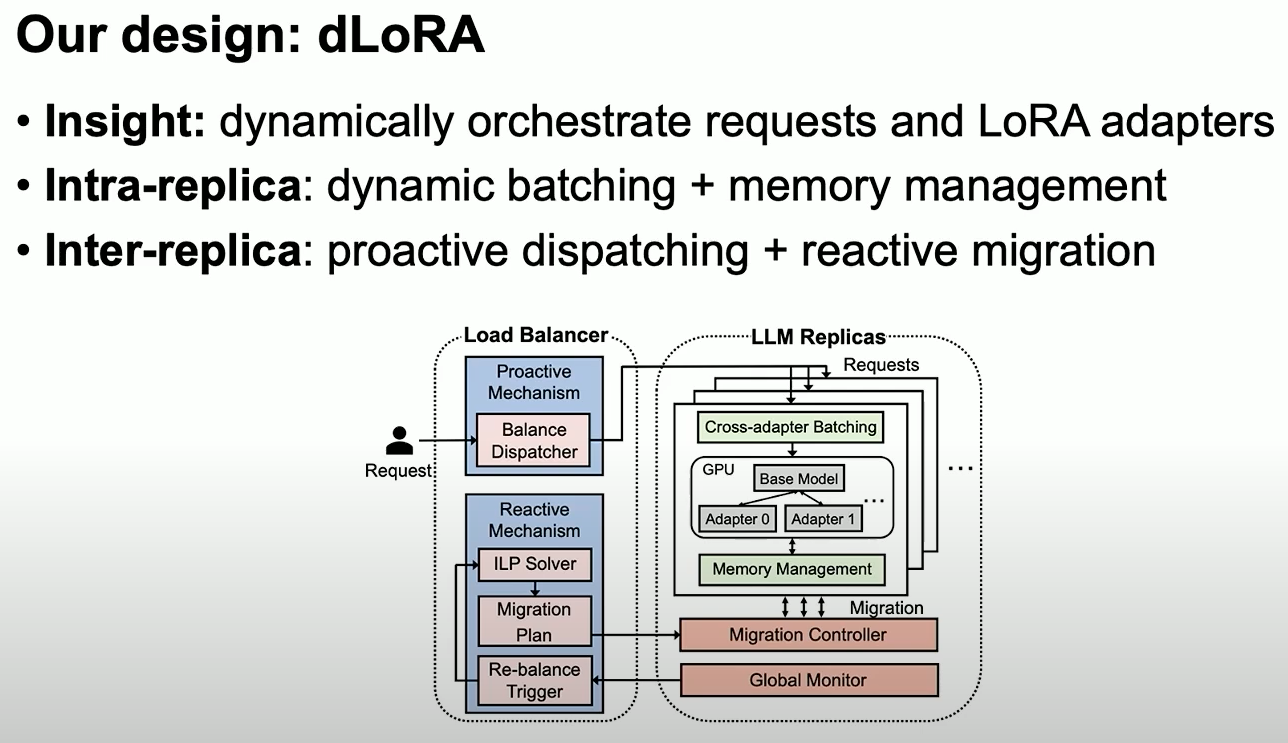
dLoRA
- 问题
- 不同类型的请求与 LoRA merge/unmegre 的时机没有很好的调度,GPU 使用率很低。
- 方法
- dLoRA可以通过�动态的调度requests和LoRA adapters实现高效的推理性能
- 基于 credit 的 batching算法决定何时 merge、unmerge,动态地从 base model 中 merge/unmerge LoRa adapters
- request-adapter co-migration algorithm 决定何时 mirgate ,动态地在不同的worker实例间调度 migrate 请求与adapters
- dLoRA可以通过�动态的调度requests和LoRA adapters实现高效的推理性能
- 结果
- 与vLLM和HuggingFace FEFT相比,throughput提升了57x和26x
S-LORA: 并行推理上千个LoRA Adapters
核心需求
- how to serve these fine-tuned variants at scale remains unexplored
- study how to scalably serve thousands of LoRA adapters on a single machine.
问题
- LoRA is often employed to adapt a base model to a multitude of tasks
挑战与解决方案
- GPU内存有限,考虑服务尽可能多的LoRA数量,要把LoRA放在主机内存中必要时交换到GPU显存中,容易造成内存碎片和不连续的内存,需要内存管理
- Unified Paging 设计了内存池,管理LoRA和KV Cache,减少内存碎片
- 要对不同的LoRA(不同的内存rank和非连续的内存)做batching很难,需要考虑新 CUDA 计算kernel
- 设计了新的 Heterogeneous Batching,自定义CUDA算子对非连续内存中LoRA进行计算,使之与内存池对齐
- 单机多GPU需要设计新的tensor 并行策略,要考虑到通信和内存��开销
- introduces a novel tensor parallelism strategy 调度小向量的通信,融合大向量和base mode的通信
结果
- 与 HuggingFace PEFT 吞吐量提高 30x,与 vLLM 的原生 LoRA 相比吞吐量提高了4倍,服务的Adapters数量增加了几个数量级(by several orders of magnitude. )
- 可以以小开销在单块 GPU 或多块 GPU 的服务器上服务数千个 LoRA adapters
评估方法
- Throughput, first token latency, and SLO
- The throughput and average request latency
- Ablation study comparing adapter merging and on-the-fly compute
- Early abort strategy experiments
Fairness in Serving Large Language Models, OSDI '24
问题
- 以前的研究只考虑了性能,但是没有考虑公平
- 不同用户的请求量,请求的 load 不同,如只有请求级别负载均衡(如FCFS),那么请求量小的用户会比请求量大的用户获得执行的几率低。
- 如果平均rate limit,但 rate limit会导致请求量大的用户无法被满足,即使服务器的负载没有打满。
目标
- GPU资源不被浪费
- 请求量大的用户可以在GPU资源有限的情况被服务
- 要isolation和utilization中做平衡。非高请求用户的资源应当分配给高请求用户。
评估方式
- 建立cost function,
w(t1, t2)=wpnp+wqnq- 也可以使用其他的cost function,
More advanced metric: piece-wise linear fucntions
- 也可以使用其他的cost function,
- 定义fairness
- backlogged的用户不应该获得比其他用户少的资源。
- 两个backlogged用户的资源应该一致。
- 实验
-
对比实验
- FCFS(First Come First Server)
- RPM(Request rate limit)
- LCF(Least Counter First):维护counters,在rejoin的时候没有counter lift
-
负载:真实负载和仿真负载
-
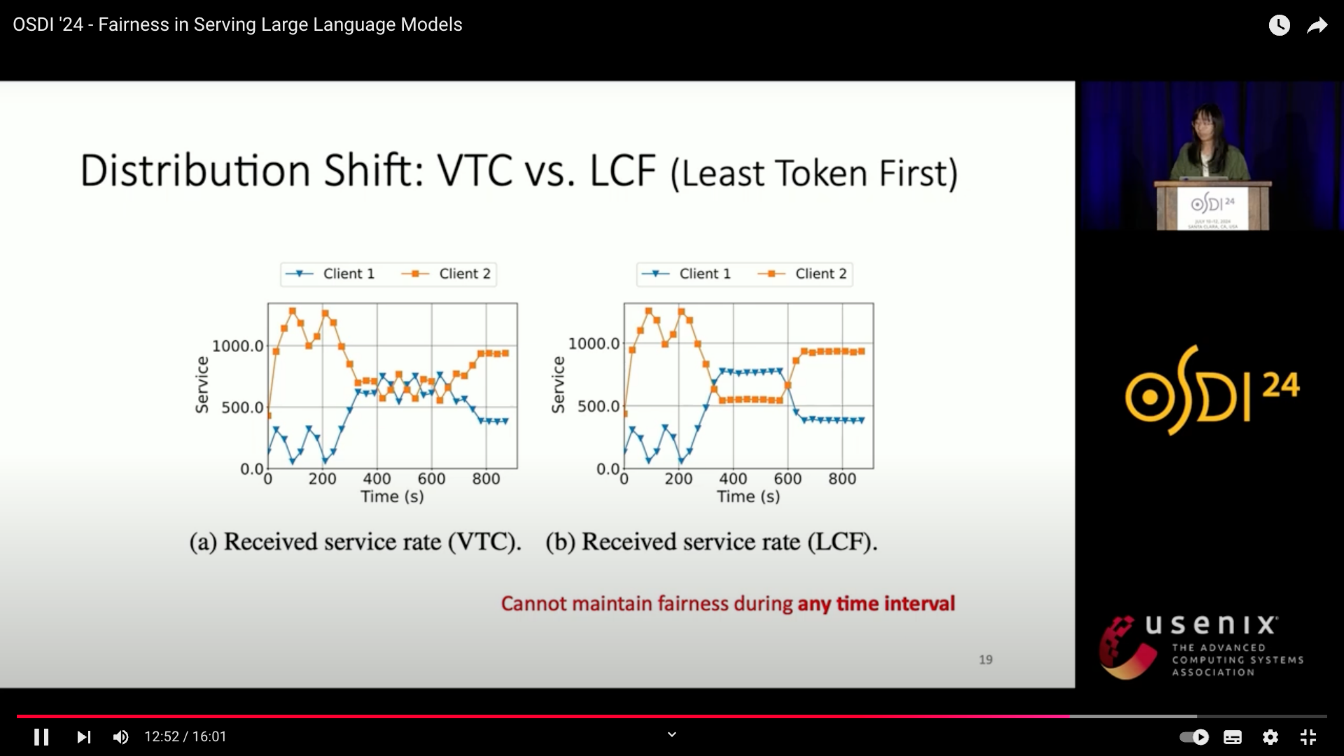
主要比较了在不同的req_rate下,不同的机制的response time变化,VTC是更fair的
-
实验效果表明
-
response time over time
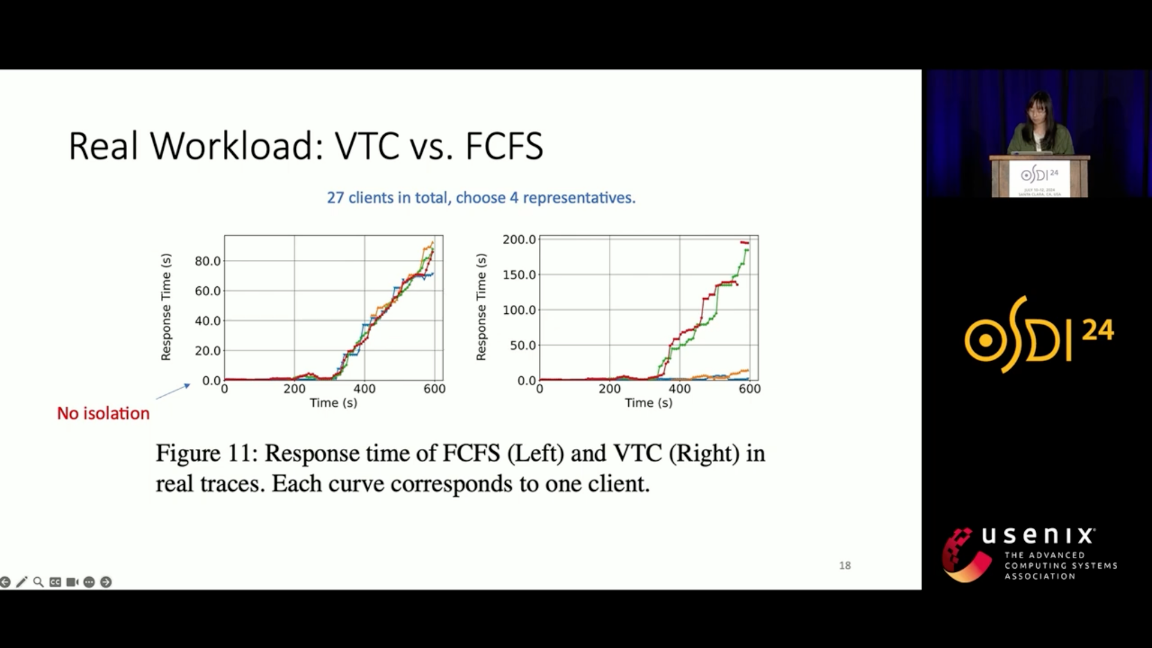
service rate over time
SLoRA: Federated Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning of Language Models
https://github.com/S-LoRA/S-LoRA?tab=readme-ov-file
lightLLM https://github.com/ModelTC/lightllm
focus on the efficiency of FL and problems of clients’ heterogeneous data distribution for pre-trained language models
需求
- In the absence of centralized data, Federated Learning (FL) can benefit from distributed and private data of the FL edge clients for fine-tuning.
问题
- Due to the limited communication, computation, and storage capabilities of edge devices and the huge sizes of popular transformer models, efficient fine-tuning is crucial to make federated training feasible
- as the data across users becomes more diverse, the gap between fully fine-tuning the model and employing PEFT methods widens.
- high heterogeneous data scenarios
- asking the clients to fine-tune the models and communicate the update has downsides. (computationally expensive as it might change the parameters of the entire model)
- supporting multi-tasks can also be challenging, especially in memory-constrained scenarios (e.g., for edge devices)
方案
- This work explores the opportunities and challenges associated with applying parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods in different FL settings for language tasks.
- overcomes the key limitations of LoRA in high heterogeneous data scenarios through a novel data-driven initialization technique.
结果
- SLoRA achieves performance comparable to full fine-tuning, with significant sparse updates with approximately ∼ 1% density while reducing training time by up to 90%
为什么需要 Finetuning?models require fine-tuning to enhance their performance on these domainspecific tasks
PEFT methods can be broadly classified into two main categories based on the nature of the tuned parameter.
- The first category fine-tunes a subset of existing parameters, including
- the classification head, bias term etc
- sparse subnetworks within the original pre-trained
- The second category is module-based fine-tuning, where an additional set of parameters (e.g., modules) are added for each task. These modules are fine-tuned while freezing the entire pre-trained model.
While the previous works focused on vision and vision-language models, our study differs in several key aspects.
- Firstly, we specifically study the application of PEFT in the context of language models and additionally examine the effect of data heterogeneity across clients on the performance of PEFT for NLP tasks.
- Secondly, our work extends beyond benchmarking different PEFT methods in the federated setting to propose an approach that yields comparable performance to FFT even in extreme non-IID settings.
Reference
- LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685
- dLoRA: Dynamically Orchestrating Requests and Adapters for LoRA LLM Serving https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi24/presentation/wu-bingyang
- Fairness in Serving Large Language Models https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi24/presentation/sheng
- SLoRA: Federated Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning of Language Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.06522
- 【LLM系列 | PEFT】什么是LoRA?
- PEFT与LORA介绍